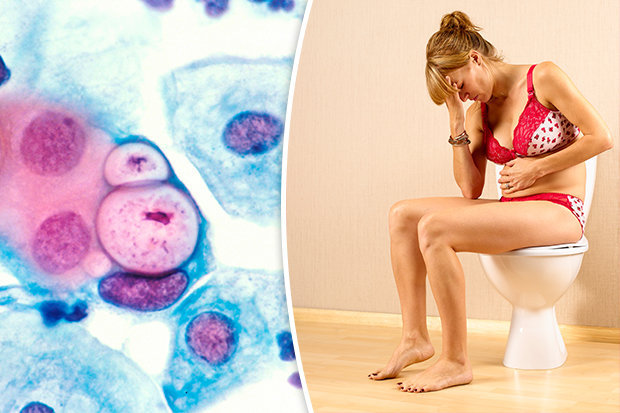
Chlamydia is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by a tiny bacterium, chlamydia trachomatis.
It is the most common STI in the UK and the number of cases is still rising year-on-year.
One of the main problems is that Chlamydia is often referred to as the “silent disease” because it can spread without any obvious signs.
If symptoms do occur, they usually come to light one to three weeks after infection.
However, in both men and women the symptoms can disappear in a few days. This is why it’s extremely important to know the warning sings to look out for and to get regular check-ups.
Today is World Sexual Health Day, 24 hours dedicated to raising awareness and breaking taboos.
We’ve already answered some of your most embarrassing sexual health questions, and here we reveal the most common symptoms of Chlamydia in men and women.
Symptoms in women:
At least 70% of women with chlamydia don’t notice any symptoms. If they do get symptoms, the most common include:
1. Pain when urinating
2. Unusual vaginal discharge
3. Pain in the tummy or pelvis
4. Pain or bleeding during sex
5. Bleeding after sex
6. Bleeding between periods
7. Heavier periods than usual
If chlamydia is left untreated, it can spread to the womb and cause a serious condition called pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). This is a major cause of ectopic pregnancy and infertility in women.
Symptoms in men:
At least half of all men with chlamydia don’t notice any symptoms. If they do get symptoms, the most common include:
1. Pain when urinating
2. White, cloudy or watery discharge from the tip of the penis
3. Burning or itching in the urethra (the tube that carries urine out of the body)
4. Pain in the testicles
If chlamydia is left untreated, the infection can cause swelling in the epididymis (the tubes that carry sperm from the testicles) and the testicles. This could affect your fertility.

If you experience any of these symptoms visit your GP, community contraceptive service or local genitourinary medicine (GUM) clinic as soon as possible.
Even if you don’t have symptoms you should get checked regularly if you are sexually active.
The NHS recommends under 25s get tested for Chlamydia once a year or every time you have a new partner.
The tests for Chlamydia are very simple. A swab test can be taken, in which a cotton bud is gently wipes over the are which could be infected, or you can urinate in a container which will be sent off for testing.